How To Use Syringe Filter
Syringe filters are single-use, membrane-based equipment. They are ideal for eliminating particle contaminants from tiny liquid and gas samples.
In this article, discover out about the advisable fabric and size of the syringe filter. Additionally, detect how to choose the perfect syringe. Equally well as the difference between sterile and non-sterile syringes.
Which material should you use for a syringe filter?
At that place are many materials you lot can cull from. Hither are some of the most common ones:
Cellulose Acetate(CA)
Cellulose acetate (CA) has an fantabulous flow rate. Still, they have a limited poly peptide binding chapters. As well, a little protein is making them platonic for protein recovery applications.
Although they have weak solvent resistance, they are hydrophilic. Since the material is hydrophilic, it is ideal for aqueous and alcoholic media. CA has a pH range of 4 to 8.
Some of the characteristics are:
Rapid mechanical strength, high flow rates, and depression extractable levels characterize cellulose nitrate. Equally a effect, it's a fantastic selection for trace element analysis. Protein bounden is high. It also has a pH range of 4 to 8.
Regenerated Cellulose (RC)
Regenerated cellulose (RC) is cellulose renewed without whatsoever wetting agents. Resistant to a wide range of solvents chemically.
Besides, the cellulose'southward wet forcefulness is loftier. Considering it is hydrophilic, information technology suits both aqueous and organic samples. But, protein binding power is relatively poor. pH levels vary from three to 12.
Glass Microfibre Filter (GMF)
GMF is a chemically inert membrane with larger pore diameters than conventional membranes. As a result, GMF is robust mechanically and resistant to organic solvents.
Potent acids (especially hydrofluoric acid) and bases are not recommended. Merely, strong acids are often used as a pre-filter. Earlier a membrane filter for high particle solutions.
In that location is ane affair about GMF. It has lower precise retention effectiveness than membrane filters.
Nylon
Nylon is a hydrophilic, flexible, tear-resistant, and autoclavable membrane filter. They tin withstand a multifariousness of organic solvents and are excellent for high pH samples. The protein binds nylon. Acidic solutions are not recommended; the pH range is 3-14.
Polyethersulfones (Human foot)
Polyethersulfones (PES) is a textile for a wide range of aqueous and organic solvents. It is hydrophilic, stable at low pH, depression in extractable, and has a low protein binding.
PES membranes have a greater liquid flow rate than PTFE membranes. Thus, it can withstand extreme temperatures. A pH range of three to 14 (sometimes quoted equally 1-fourteen).
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a hydrophobic material. You can utilize it with a broad range of solvents. Use it even with aggressive solvents, with difficult-to-filter solutions similar extremely acidic samples.
Tolerance to estrus and mechanical stress is loftier and consequent. Information technology has a pH range of approx. 1-14.
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has:
one. High tensile strength,
two. Potent solvent resistance,
three. Low protein binding,
Which makes it ideal for biomedical filtering, sterilizing filtration, and HPLC sample training. pH levels vary from 1 to 14.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE is platonic for filtering gaseous or organic solvent-based samples and corrosive metals.
Because it'southward hydrophobic, it's resistant to hostile media. Information technology also has excellent temperature stability, allowing for a broader sample range.
When working with watery materials, the membrane generally has to exist pre-wetted. Y'all can moisture the membrane with a small corporeality of alcohol. You may also use information technology to continue moisture out of air vents. pH levels vary from 1 to fourteen.
Hydrophilic PVDF and PTFE
We talked almost the hydrophobic PTFE and PVDF above.
The hydrophobic type of syringe filter is generally used for gas filtration.
If nosotros use hydrophilic blazon PTFE or PVDF, it ways we demand to apply it to filtration of liquids (organic solvents, strong acids, alkalis, and aqueous solutions).
Information technology is too possible to filter organic solvents using hydrophobic membranes, such as ethanol, etc. As a general rule, liquids that tin exist filtered with a hydrophobic type can also be filtered with a hydrophilic type. So, hydrophilic filters are recommended for filtration of liquids.
Which Size of a Syringe Filter Should You Utilize?
It would be best to look at a few things when choosing the right syringe filter.
The majority of syringe filters come in a diversity of pore diameters. And then, it's critical to ensure the pore size is right for your application to work.
Below are the most frequent pore sizes found, equally well equally samples of typical uses:
0.1m – mycoplasma elimination and solution sterilization
0.2/0.22m – sterilization of the solution (bacterial removal)
0.45m – filtration and particle reduction in general
>0.45m – often used as a pre-filter
Next, cull a proper diameter.
The full corporeality you tin filter via a given diameter syringe filter can vary. That is because high particulate-loaded samples tend to clog membrane pores faster.
For samples of less than 10ml, use a 13mm diameter tube.
For models of less than 100ml, use a 25mm bore tube.
For pieces of less than 250ml, use a 33mm diameter tube.
Step-past-Pace Guide on How to Cull a Syringe Filter
Here is a quick guide on choosing the right filter for your syringe.
ane. Footstep – Determine if Your Application Requires Pre-Filtration
Prefiltration is often known as screening or coarse filtration. It is a method of removing large particles and waste product from membrane filtration systems.
You can use prefiltration on the entire membrane filtration arrangement. You tin apply it also on individual membrane units.
The pore size used in the prefiltration process varies based on:
1. The kind of membrane filter system used
two. The quality of the input water.
two. Step – Select an Appropriate Membrane Type
Here is a quick guide on selecting a proper membrane-blazon made by airekacells.
Source: airkacells
three. Footstep – Select an Appropriate Filter Diameter
Filter inlets come up in three sizes. Also, they are female Luer-Lock suitable and characteristic inert polypropylene housings. The diameter determines the volume, which you tin filter.
Yous can choose between 13, 25, and 33mm filter diameters, every bit explained to a higher place.
iv. Step – Now, Select a Proper Pore Size
For research and medical purposes, 0.2/0.22 μ and 0.45 μ syringe filters are the about often used pore sizes.
The particle size determines the pore size you use. For example, utilize a syringe filter of 0.ii-micron pore size to filter out particles larger than 0.two microns in bore.
Another method for determining column micron size:
– use 0.45 μ for microns greater than 3 μ
– use 0.22 μ for microns less than three μ
0.45 μ membranes:
– for filtering and particle removal
0.22 μ membranes:
– for solution sterility (leaner removal)
v. Stride – Is it Better to Accept a Sterile or Non-Sterile Syringe Filter?
Check beneath for details on sterile and not-sterile syringe filters.
Y'all tin use sterile or non-sterile syringe filters for particulates removal. Make the decision based on the following operating applications:
– If you demand a sterilized solution, utilise a sterile syringe filter. Those filters ofttimes come separately packed. They provide the almost fantabulous performance without contamination.
– Use a non-sterile needle filter if you program to sterilize the solution. Non-sterile filters are much cheaper.
Let'southward talk more about sterile and non-sterile syringe filters.
Sterile and Non-Sterile Syringe Filters
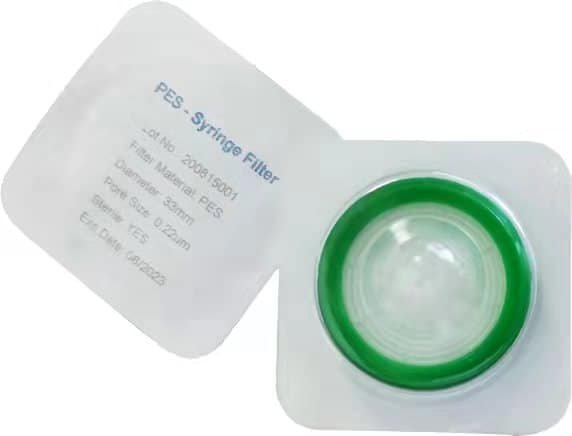
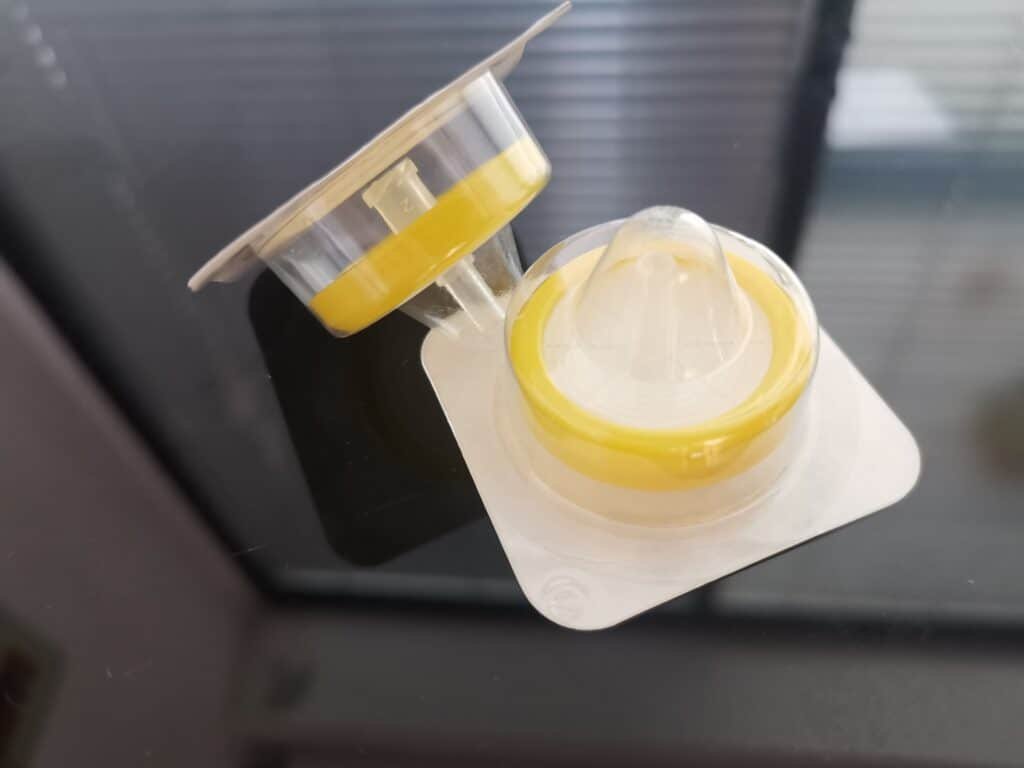


You can find a sterile filter at the end of a syringe. That filter removes all particles from a sample before the test.
Scientists use testing applications in a variety of industries, such every bit:
ane. Pharmaceutical industry
2. Biotechnology industry
3. Agricultural laboratories
So, in analysis, non-sterile syringe filters can help you get the well-nigh out of your equipment.
1. UHPLC,
two. LC-MS
3. Ion chromatography
iv. Dissolution testing
In Which Cases Do You lot Utilise a Sterile Syringe Filter in General?
Use a sterile syringe filter for sterilizing liquids or purifying sterilized solutions.
What is the Application of the Sterile Syringe Filter
The sterile syringe filter is primarily used for:
1. Sample pre-clarification,
2. Particle removal,
3. Liquid and gas sterilization filtering,
4. Laboratory biological fluid,
v. Civilization medium and medium additives sterilization filtration,
six. Other similar applications.
So, what is the application of the sterile syringe filter?
1. Analyze the ambient air quality, frazzle gases, and h2o.
2. To filter out particles, the medical business requires:
a) Autoclave sterilization water injection
b) Effective infusion solution.
Information technology tin increase the internal quality of medications and the clarity pass rate.
three. Detection and analysis of:
a) Food,
b) Beverage,
c) Medicinal raw materials,
d) Completed appurtenances
f) Semi-finished products.
4. Filtration of water and organic solutions in educational and commercial R&D laboratories.
5. Sample preparation for chromatography and mass spectrometry; pedagogy, quality inspection, and quality control
How Long do Syringes Stay Sterile?
A typical syringe filled with medication is sterile for almost 12 hours.
When Should You lot Use a Non-Sterile Syringe Filter?
Use a not-sterilized syringe filter for routine filtering and sample purification.
You tin can use non-sterile syringe filters for:
- Pre-filtration
- General filtration
- Analytical sample grooming applications
How to Use a Syringe Filter? Pace-by-Step Guide
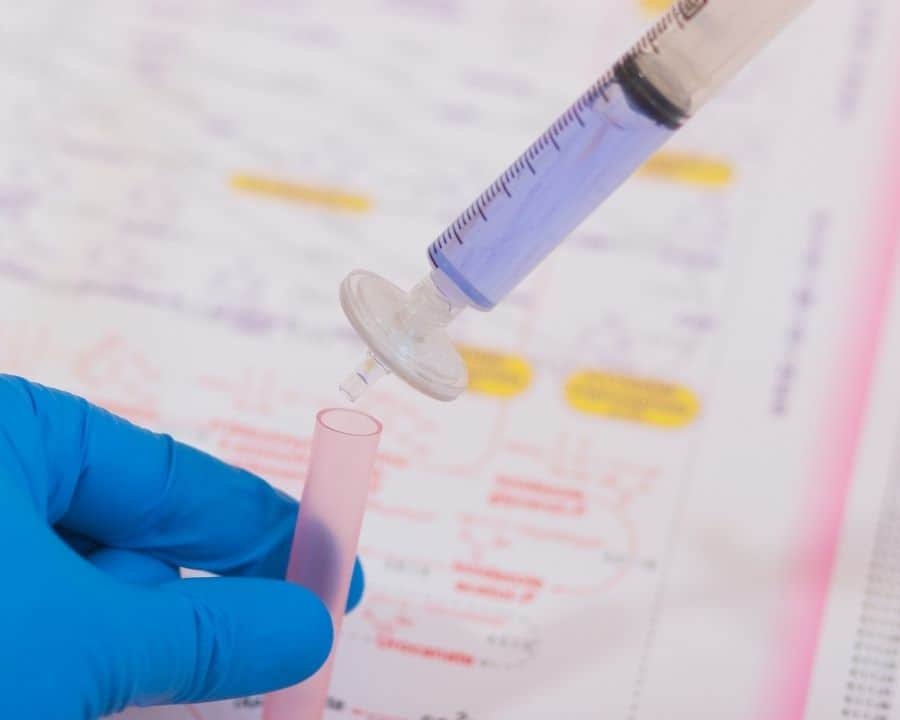
one. Fill the syringe with the sample.
2. Using a twisting motion, secure the filter. This is roughly 1-quarter turn with a Luer slip syringe as the filter is pressed. If the needle has a Luer lock (as in this instance), tighten it simply not too much.
3. Hold the syringe upright and filter vertically to moisten the membrane. Avoid air obstructions past dispersing the sample throughout the membrane surface.
4. Printing the syringe plunger to laissez passer the sample through the filter.
If possible, drop the showtime 0.25-0.5ml of the sample. Since any contamination will most likely be in the first few microlitres. Supplant the filter if the backpressure rises since it may have clogged. Excessive pressure might crusade the filter housing to outburst, and so be careful.
5. Change the filter and repeat the process for the following sample.
"Air-Purge"
If you have a pocket-size sample, you can decrease the loss in the syringe past using the "air-purge" approach.
Before filling the syringe with the sample solution, pull a little quantity of air into it. Apply this air to purge the filter, ensuring that but the tiniest corporeality of sample remains in the filter.
Contagion
If you're concerned about contamination, syringe filters can cause contamination at low levels.
Before filtering the sample through the same filter, launder information technology with ultra-clean h2o. Or wash information technology with a mild (ane percent) acrid solution to limit the quantity of contamination.
Y'all may need to echo this process several times to thoroughly "clean" the filter.
What to Look Out for When Using Syringe Filters?
1. Cleanse the new syringe filter to avoid contagion. Cleanse it with detergent, sterilize it, disinfect, and clean it with high-temperature steam.
2. Before using the syringe filter, ensure the attachments and the sealing ring are present and undamaged. Install it as needed.
3. The cylinder'south pressure gauge is a liquid pressure brandish gauge. Thus, using a secondary filter allows the syringe filter pressure gauge index to be lower.
The force per unit area will ascent, and the period rate volition fall as the filter's fourth dimension increases. That indicates that the bulk of the holes in the filter element have been plugged. That ways y'all need to flush them or supervene upon them with a new filter element.
4. Practise non connect the inlet and outlet of the syringe filter backward while installing it.
The clean liquid output port links to the filter element socket. The liquid inlet port is on the pipe filter bottom plate side.
5. Make sure the filter element is upright before placing it into the port. The pressure plate bends the fins and tightens the screws once you insert the port.
Yous should turn the filter chemical element of the 226 interfaces xc degrees and clamp information technology afterward the archway. This is the most crucial stride in the installation process.
If yous're not cautious, the seal won't hold, and the water will leak, which won't fulfill your needs.
half dozen. The manufacturer packed the replacement filter element in a clean production facility. And in a plastic bag.
Before using, do not rip the plastic packaging. Instead, utilize a more demanding filter element. Afterward installation, sterilize it with high-temperature steam.
7. When the liquid enters the syringe filter, plough on the vent switch to make full the cylinder with the liquid. Otherwise, the filtering effect will be poor.
Conclusion
In this commodity, we accept already discussed the blazon of material, the size, and the appropriate employ of syringe filters. For more details on the different kinds of syringe filters that Mastelf offers, Just CLICK here. Here, you can get everything you need.
How To Use Syringe Filter,
Source: https://www.mastelf.com/how-to-choose-a-syringe-filter/
Posted by: couturesaut1950.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Syringe Filter"
Post a Comment